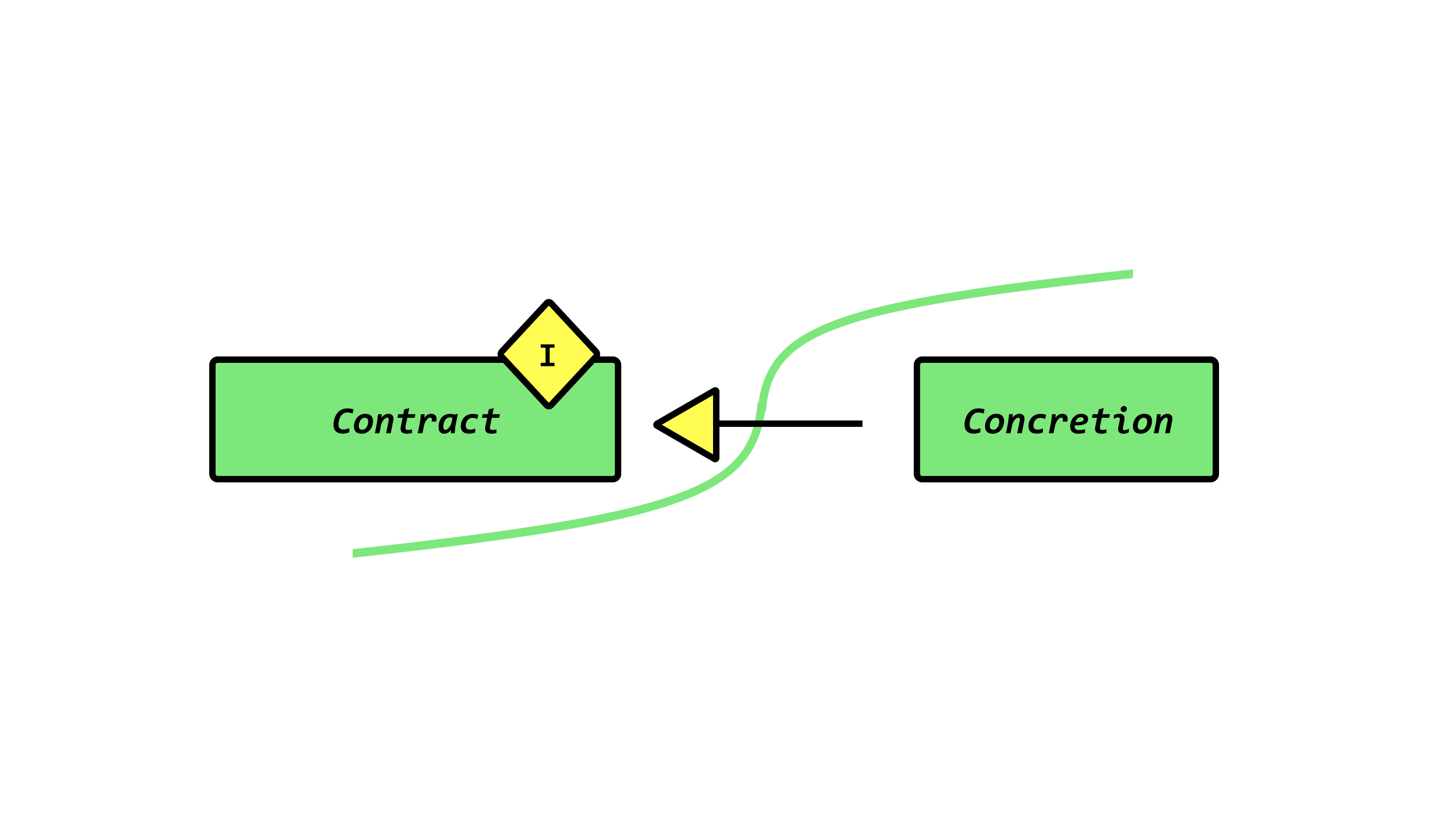
What are Dependencies, Composition, Delegation, and Aggregation in Object-Oriented Programming?
Dependency: The Address object comes from outside, it's allocated somewhere else. This means that the Address and Employee objects exists separately, and only depend on each other.
Composition: Here you see that a new Engine is created inside Car. The Engine object is part of the Car. This means that a Car is composed of an Engine.
Composition is about the relationships between objects.
Delegation is about passing work from one object to another.
These are actually different (but sometimes related) concerns.
What you've got is B composed of A (B refers to A).
Aggregation & composition: An aggregation is an object that represents a concept as a whole and handles managing how its parts are accessed and changed. Composition is related but it adds an additional meaning to aggregation. Composition says that parts of the aggregation can’t exist independently (ie: a wheel can’t exist unless it belongs to a car).
So dependency == aggregation? stackoverflow.com/questions/11881552/… – danihodovic Jan 9, 2014 at 15:04 @dani-h No, aggregation and composition describe how things are build/structured, while dependency is more a property of a certain structure. See @TheLostMind's great answer
Discussion
Liked this? Sing it loud and proud 👨🎤.
Stay in touch!
Join 15000+ value-creating Software Essentialists getting actionable advice on how to master what matters each week. 🖖
View more in Object-Oriented Programming
You may also enjoy...
A few more related articles